what is ketone in chemistry Ketone formula structure definition ketones formation study group functional diabetestalk aldehyde
Ketones are a class of organic compounds characterized by the presence of a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to two other carbon atoms. They are widely used in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, fragrances, and solvents. One important reaction involving ketones is the Clemmensen reduction. This is a chemical reaction that converts ketones into hydrocarbons by reducing the carbonyl group to a methylene group (CH2) using zinc amalgam and hydrochloric acid. The Clemmensen reduction is an important tool in organic synthesis and is often used to prepare alkanes from ketones. The mechanism of the Clemmensen reduction involves the addition of zinc amalgam to the carbonyl group of the ketone, followed by protonation and reduction. The zinc amalgam acts as a reducing agent, while the hydrochloric acid provides the protons necessary for the reaction. One interesting aspect of the Clemmensen reduction is that it only works for ketones, not aldehydes or other related compounds. This is due to the fact that the zinc amalgam reduces the carbonyl group all the way to a methylene group, which is not possible with aldehydes or other compounds. Another important aspect of ketones is their reactivity with nucleophiles. The carbonyl group of a ketone is electrophilic, meaning that it is attracted to electron-rich regions of other molecules. This property makes ketones a useful starting material for a wide range of reactions, including the Grignard reaction and nucleophilic addition. The Grignard reaction is a powerful tool in organic synthesis that involves the addition of a Grignard reagent (an organomagnesium compound) to a ketone to form an alcohol. The Grignard reagent acts as a nucleophile, attacking the electrophilic carbonyl group of the ketone and forming a new carbon-carbon bond. Nucleophilic addition is another important reaction involving ketones. This reaction involves the addition of a nucleophile to the carbonyl group of a ketone, resulting in the formation of a new carbon-carbon bond. Nucleophiles can be either negatively charged (such as a hydroxide ion) or neutral (such as an amine). In conclusion, ketones are an important class of organic compounds with a wide range of uses in various industries. The Clemmensen reduction is an important tool in organic synthesis, while the reactivity of ketones with nucleophiles makes them useful starting materials for a wide range of reactions.
If you are searching about What is Ketone? - Definition, Structure, Formation & Formula - Video you’ve visit to the right page. We have 5 Pictures about What is Ketone? - Definition, Structure, Formation & Formula - Video like Ketone supplements enhance non-toxic cancer therapy - ScienceBlog.com, Clemmensen Reduction Chemistry: Definition, Explanation & Mechanism and also Ketone supplements enhance non-toxic cancer therapy - ScienceBlog.com. Here it is:
What Is Ketone? - Definition, Structure, Formation & Formula - Video
 study.comketone formula structure definition ketones formation study group functional diabetestalk aldehyde
study.comketone formula structure definition ketones formation study group functional diabetestalk aldehyde
Ketone - Chemistry LibreTexts
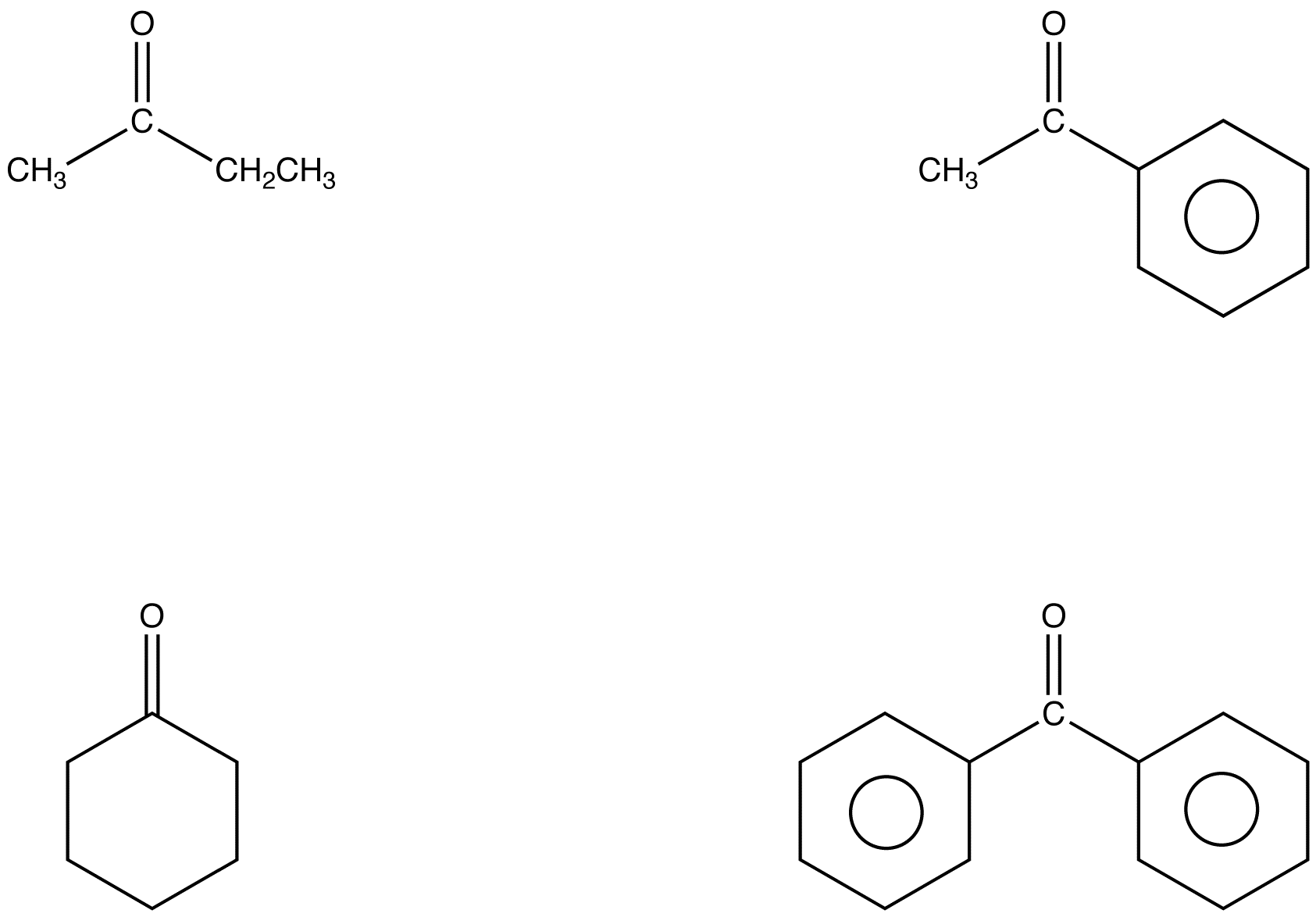 chem.libretexts.orgketone chemistry carbonyl group keto called chem libretexts organic ochempal chemwiki
chem.libretexts.orgketone chemistry carbonyl group keto called chem libretexts organic ochempal chemwiki
Ketone Supplements Enhance Non-toxic Cancer Therapy - ScienceBlog.com
 scienceblog.comketone ketoacidosis chetoni ketosis acid cetona butanone ketogenic urine cetoacidosis compound aldehyde aldehydy scienceblog alchohol carboxylic dipende skeletal metil grupa
scienceblog.comketone ketoacidosis chetoni ketosis acid cetona butanone ketogenic urine cetoacidosis compound aldehyde aldehydy scienceblog alchohol carboxylic dipende skeletal metil grupa
Clemmensen Reduction Chemistry: Definition, Explanation & Mechanism
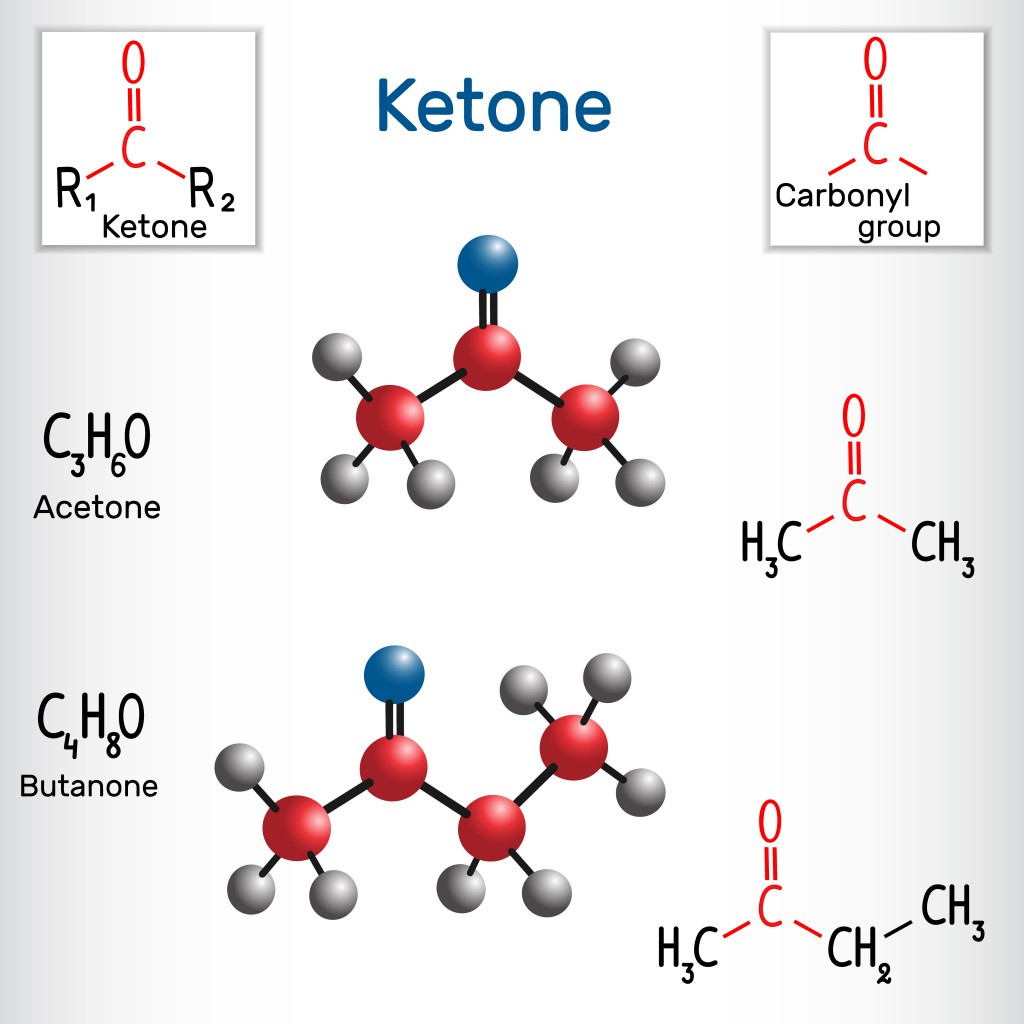 www.scienceabc.comketone formula ketones structural reduction molecule clemmensen ethyl chemical chemistry butanone acetone vector methyl mechanism occurring jasmine commonly camphor spearmint
www.scienceabc.comketone formula ketones structural reduction molecule clemmensen ethyl chemical chemistry butanone acetone vector methyl mechanism occurring jasmine commonly camphor spearmint
What Is Ketone Formula? | DiabetesTalk.Net
 diabetestalk.netketone formula diabetestalk
diabetestalk.netketone formula diabetestalk
Ketone formula structure definition ketones formation study group functional diabetestalk aldehyde. Ketone supplements enhance non-toxic cancer therapy. Ketone chemistry carbonyl group keto called chem libretexts organic ochempal chemwiki